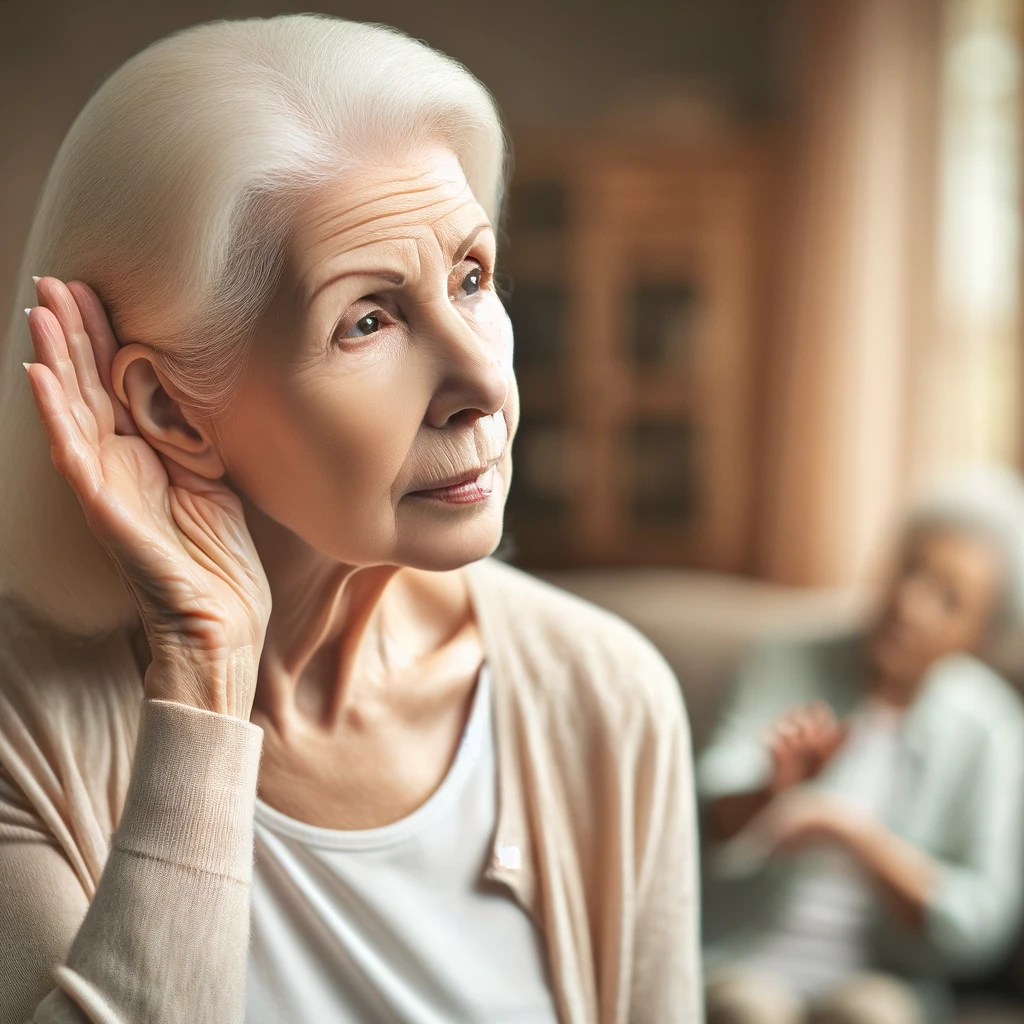

Hearing loss is a prevalent issue that affects many seniors, significantly impacting their quality of life. As we age, the risk of experiencing some degree of hearing impairment increases. Understanding, identifying, and addressing hearing loss in aging is crucial for maintaining a healthy, active, and engaged lifestyle during the senior years.
Understanding Hearing Loss in Aging
Definition and Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss in seniors, medically known as presbycusis, typically involves the gradual loss of hearing. It can be categorized into three types: conductive (related to problems with the ear canal, eardrum, or middle ear), sensorineural (related to problems of the inner ear), and mixed (a combination of conductive and sensorineural).
Prevalence of Hearing Loss in the Elderly
As people age, hearing loss becomes increasingly common. It is estimated that approximately one in three people between the ages of 65 and 74, and nearly half of those over 75, experience hearing loss.
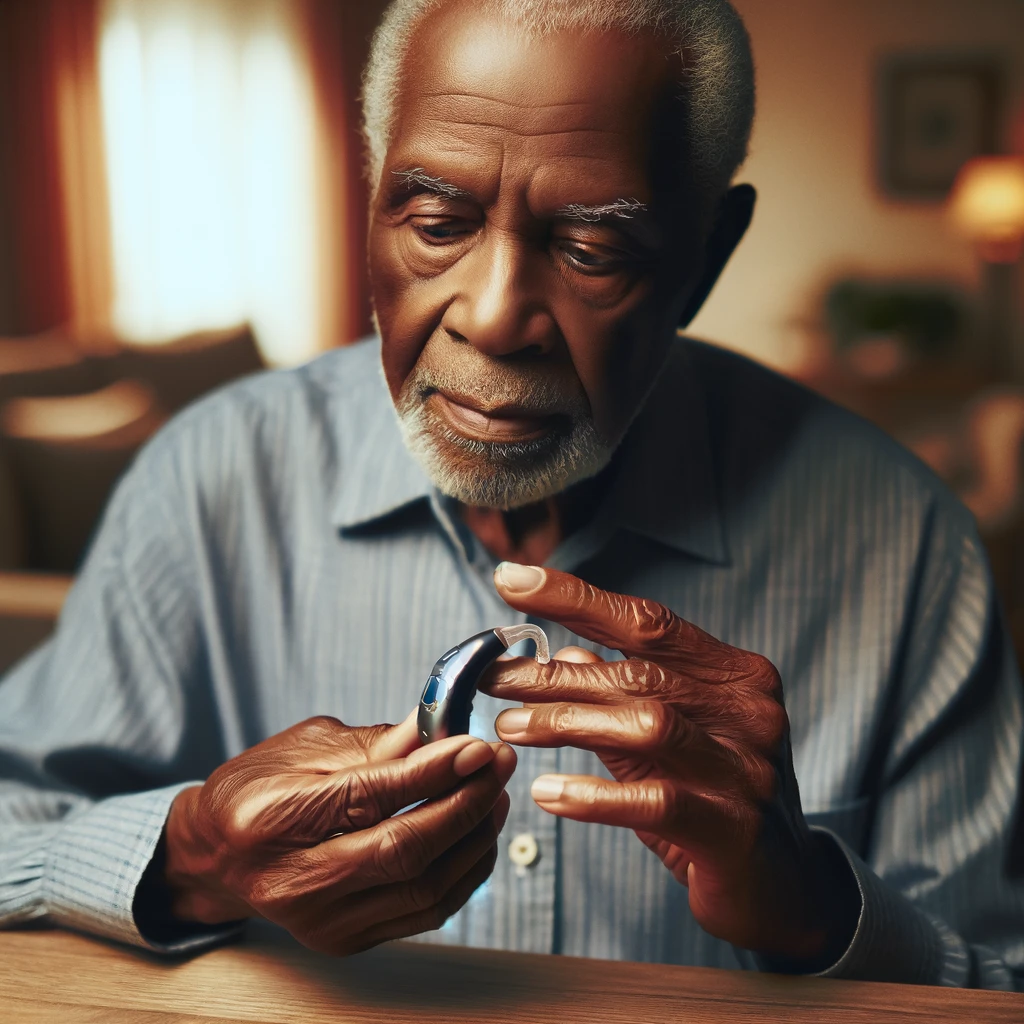

Causes of Hearing Loss in Seniors
Age-related (Presbycusis)
This is the most common cause of hearing loss in seniors, occurring as a part of the natural aging process. It involves the gradual loss of hearing as inner ear structures deteriorate over time.
Environmental Factors
Long-term exposure to loud noises, whether in the workplace or through recreational activities, can contribute to hearing loss in later years.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain medications, can also contribute to hearing loss in seniors.
Symptoms of Hearing Loss
Recognizing the symptoms is key to early intervention. Common signs include difficulty hearing in noisy environments, frequently asking others to repeat themselves, and turning up the volume higher than usual on the television or radio.
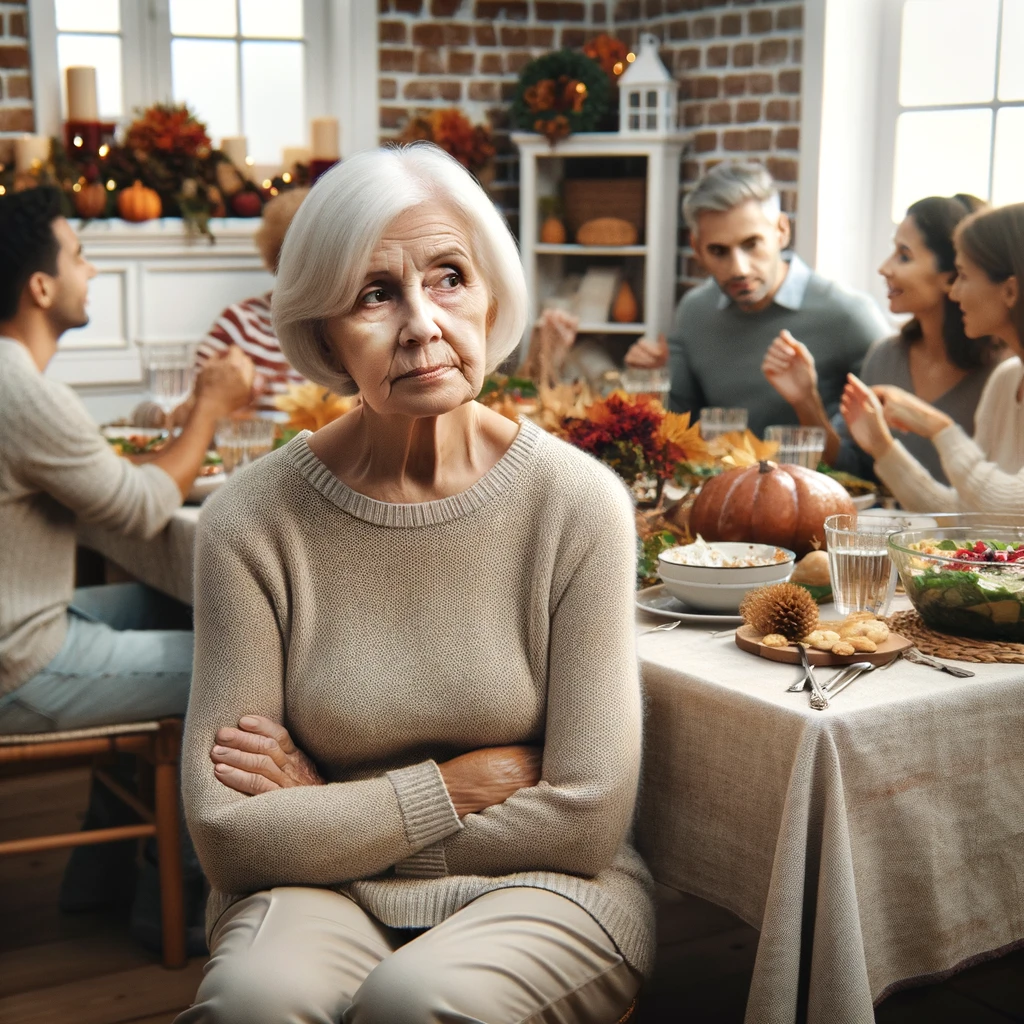

Impact of Hearing Loss on Senior Health
Psychological Effects
Hearing loss can lead to social isolation, as individuals may avoid social interactions due to difficulty in communication. This isolation can, in turn, lead to depression and anxiety.
Physical Effects
Hearing impairment can affect balance and increase the risk of falls and injuries among seniors.
Cognitive Effects
There is growing evidence linking hearing loss to cognitive decline and dementia, making it even more crucial to address hearing health.
Preventing and Mitigating Hearing Loss
Preventive Measures
Protecting ears from loud noises and having regular hearing check-ups can help prevent or delay the onset of hearing loss.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection can significantly improve the effectiveness of treatments and interventions.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can support overall ear health.

Treatment and Management of Hearing Loss
Hearing Aids
Advancements in hearing aid technology have made them more effective and less obtrusive than ever before.
Assistive Listening Devices
Devices such as amplified phones and TV listening systems can help seniors with hearing loss.
Cochlear Implants
For severe hearing loss, cochlear implants can be a viable option, providing an alternative to traditional hearing aids.
Communication Strategies
Family members can adopt specific communication strategies to better interact with loved ones experiencing hearing loss.
Living with Hearing Loss: Success Stories and Adaptations
Success stories can inspire and motivate seniors facing hearing loss. Such as the story of Steve Latus. (https://www.mountsinai.org/about/patient-stories/life-after-hearing-loss-stephen) Click the link to read about his choices and how they affected his life. Adapting to a life with hearing impairment involves both technological solutions and lifestyle adjustments. Here’s another story of hearing loss recovery (https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/cochlear-implants/patient-story-carol) which can be seen at this link.
The Future of Hearing Loss Treatment
Ongoing research in the field of audiology promises new and improved treatments for hearing loss. The role of technology, such as sophisticated hearing aids and potential regenerative therapies, is particularly promising.

Conclusion
Addressing hearing loss in seniors is vital for maintaining a high quality of life. Early detection, effective management, and embracing available treatments and adaptations can make a significant difference. It’s important for seniors and their families to be proactive in seeking help and support for hearing loss.
